In this post, you’ll grasp the fundamental syntax for opening a file and reading its contents, while learning how to retrieve data from a database and compare the details with text file. With just four straightforward steps, you can effortlessly identify the existing text file values and verify their presence within the Oracle database table.
Reding Text file from the local system
Reading or writing a file in python can be done in different ways. Most of the time we use Open() or with statements to open file and read the file.
open() is the inbuilt function used to open the file. The open() function returns a file object, which has a read() method for reading the content of the file. When we use Open() function we need to close it manually when we complete our work.
with statement provides a way for ensuring that we didn’t have to close the file manually it takes care by with statement automatically.
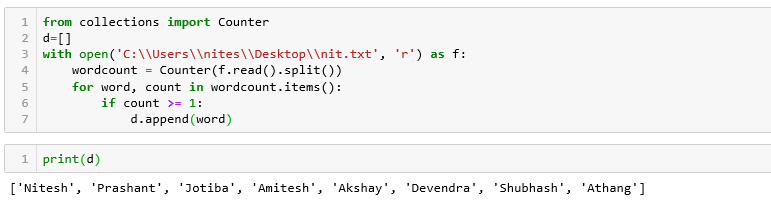
We have tried to find the word which is present in a given text file and save it into the list for further processing.
Create a table using the below script if the table does not exist in the database.
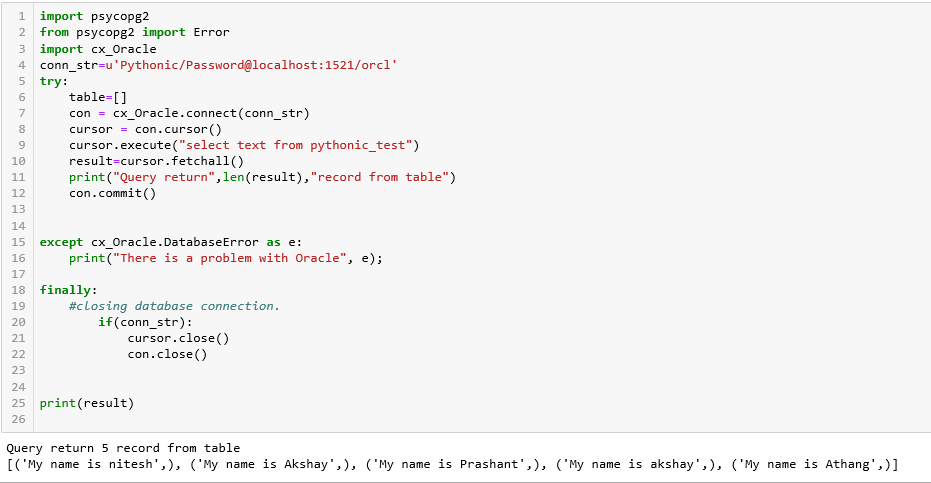
Execute the below snippet to fetch the record from the table.
To select the data from the Oracle database in python we need to follow some steps which are given below :
1.Importing cx_Oracle : This is a Python extension module that enables access to Oracle Database.
By the below command, you can install cx_Oracle package but it is required to install Oracle database to use those functions.
pip install cx_Oracle
2.Creating Connection: Establish a connection between Python program and Oracle database by using connect() method present in cx_Oracle package. Which consists of different connection credentials such as username, password, IP address, port, and database name.
3.Executing query: To execute sql query cursorobject required which help to hold the connection details and execute single or multiple query.
Fetching or Reading of data can be done using a different method
fetchone: To fetch a single row from a result set we can use cursor.fetchone(). This method returns a single record and it can return a none if no rows are available.
fetchmany: This method returns the number of rows specified by size as an argument the default value of size is 1. We can use as many we want. It returns an empty list when no rows available.
fetchall: It fatches all the rows from the table as a list of tuples. An empty list is returned if there is no record to fetch from the table.
4.Commit the transaction: If any DML(Data Manipulation Language) operation perform on database we need to commit in order to reflect the changes in database.
5.Closing Connection: We write the close function within finally block so whenever any error occurs then also it close the connection along with database operation.
Let see the below snippet for a better understanding of the above concept.
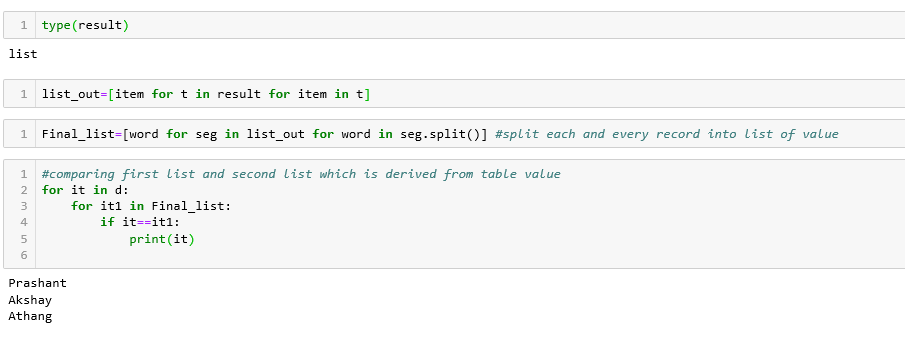
Compare the fetched record from the created table with the details present in a text file and return the matched values.
Below python query help to split and store each word which is got by our resultset in list object name as Final_list. Using for loop we compare the text word with the word extracted from the table and return the exact matched word.